Mannacote: What It Is, Why It Matters & Key Uses
In industrial, agricultural, and coating circles, Mannacote is emerging as a versatile protective / functional coating / input that claims to offer superior durability, resistance, and controlled-release behavior. Unlike traditional coatings or fertilizers, Mannacote seeks to combine performance with sustainability. This piece will:
-
Define what Mannacote is (and how different sources treat it)
-
Explain its core mechanism & technology
-
Describe major applications across industries
-
Lay out key advantages & challenges
-
Compare it to competing solutions
-
Look ahead: trends, adoption, and future potential
Let’s explore what credible sources say about Mannacote and how to interpret the concept.
What Is Mannacote? Definitions & Contexts
“Mannacote” is not a universally standardized term—its meaning varies a bit depending on the domain. Here are major usages:
-
Protective / industrial coatings: Many recent articles treat Mannacote as a high-performance coating system for surfaces exposed to extreme conditions (corrosion, chemicals, abrasion).
-
Agricultural / fertilizer / natural coating: Some websites identify Mannacote as a natural, controlled-release fertilizer or bio-coating for plants, seeds, or produce.
-
Hybrid / multifunctional coating: Others assert Mannacote can act both as a protective surface layer and embed functional benefits (e.g. antimicrobial, food preservation) depending on formulation.
Because of these overlapping definitions, when someone refers to “Mannacote,” it’s essential to clarify which variant—coating, agricultural, or hybrid—is meant.
On the official website (mannacote.com), Mannacote is presented under the umbrella of “advanced coating solutions” protecting metal, concrete, wood, and other surfaces. That suggests the industrial coating meaning is possibly the primary or dominant one in many commercial contexts.
Mechanism & Technology: How Mannacote Works
Understanding how Mannacote is claimed to function helps in judging its strengths and limitations.
Core Technology
-
In coating contexts, Mannacote is described as a polymer / resin-based protective layer that forms a tough, resilient barrier on various substrates.
-
Some versions incorporate nanoparticles, microcapsules, or self-healing capabilities—this allows the coating to respond to micro-scratches or mild damage by releasing healing agents.
-
The coatings are engineered to resist corrosion, chemical attack, thermal stress, abrasion, UV exposure, and mechanical wear.
-
In agricultural / food / bio-coating settings, Mannacote is described as a biodegradable or edible coating that delivers nutrients or protection gradually (controlled-release) to seeds, produce, or soil.
Key Functional Principles
-
Barrier formation — the coating isolates the substrate from moisture, oxygen, and corrosive agents.
-
Adhesion & crosslinking — strong adhesion and crosslinked molecular structure help resist delamination, cracking, or peeling.
-
Controlled / responsive release (in hybrid variants) — embedded agents (nutrients, antimicrobial compounds) may be released slowly or in response to environmental cues.
-
Self-healing (optional advanced version) — microcapsules break open under stress to repair minor damage or microcracks
-
Environmental resistance — UV stabilizers, pigments, additives help maintain integrity over time in sun, salt, or industrial environments.
In practice, the actual performance depends heavily on substrate preparation, coating thickness, environmental conditions, and formulation.
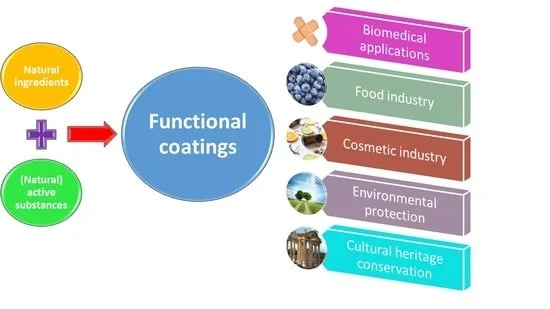
Major Applications of Mannacote
Because of its dual (or multiple) identities, Mannacote finds usage in several fields:
1. Industrial & Infrastructure Protection
This is perhaps the most prominent domain:
-
Coating metal structures, pipelines, storage tanks, machinery against corrosion, abrasion, chemical exposure.
-
Use on marine / offshore structures where saltwater, humidity, and UV stress are constant threats.
-
In power plants, refineries, chemical plants, where surfaces undergo high temperatures, chemical attack, and mechanical wear.
-
In civil infrastructure: bridges, tunnels, reinforced concrete elements — where coating helps guard against moisture ingress and degradation.
2. Agriculture, Horticulture & Food Preservation
-
Seed / grain coatings: Mannacote as a protective film on seeds to reduce pest attack, moisture damage, or premature germination.
-
Produce / fresh food coatings: A thin edible or biodegradable layer that slows moisture loss, oxidation, or microbial growth.
-
Slow-release fertilizers / soil enhancers: Some descriptions portray Mannacote as a fertilizer matrix that gradually releases nutrients into soil, improving uptake and reducing leaching.
3. Pharmaceutical / Biomedical / Packaging
-
As a controlled-release coating on tablets or capsules (for drug delivery). Some sources hint at Mannacote’s role in bio-coating or protective encapsulation.
-
In medical devices: surface coatings offering antimicrobial or corrosion resistance. (This is more speculative, but aligned with multifunctional coating claims.)
-
In packaging: coatings that maintain food freshness, barrier protection while being safer / lower-VOC / biodegradable.
4. Cross-Sector / Hybrid Use Cases
Because Mannacote is positioned as a “smart, multifunctional coating,” some use cases span sectors — e.g. equipment in agricultural settings needing both protection and slow-release of nutrients or antimicrobials.
Key Benefits & Challenges
Benefits & Strengths
-
Longevity & durability — better life span means lower maintenance and recoating frequency.
-
Multifunctionality — ability to combine protection with other functions (release, antimicrobial, etc.).
-
Resistance to chemicals, abrasion, UV — making it well suited for harsh environments.
-
Eco / sustainable variants — low-VOC, biodegradable or safer formulations in some versions.
-
Cost savings over life cycle — though initial cost may be higher, extended life and lower maintenance offset that.
Challenges & Limitations
-
High upfront cost — advanced coatings tend to cost more per unit area than conventional paints.
-
Complex application & surface prep — performance depends heavily on proper preparation, curing, and skilled application.
-
Formulation variation & standardization — since “Mannacote” covers multiple variants, ensuring the right one is used for each environment is critical.
-
Long-term behavior uncertainty — especially in newer hybrid or multifunctional use (e.g. in agriculture or pharmaceutical fields).
-
Scale and market acceptance — competing with well-established coatings and inputs, convincing industries to switch can be slow.
-
Regulatory / certification hurdles — for food, medical, or agricultural use, coatings need to meet safety, regulatory, or food-grade standards.
Mannacote vs Other Coatings / Solutions
To appreciate what Mannacote brings, comparing it to typical alternatives helps:
| Feature | Mannacote | Conventional Coatings (Epoxy, Polyurethane, etc.) |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion / chemical resistance | Very high (in claimed formulations) | Moderate to high depending on grade |
| Thermal / UV stability | Strong in advanced formulas | Often weaker, degradation over time |
| Multifunctional features | Possible (self-healing, release, antimicrobial) | Usually single-purpose |
| Environmental / health profile | Some low-VOC / biodegradable variants | Many with higher VOCs / hazardous solvents |
| Lifecycle cost | Often lower when factoring durability | Lower initial cost but more frequent recoats |
| Application complexity | More demanding | More standard, well-known process |
In many use cases where multiple stresses co-occur (corrosion + abrasion + temperature cycling), Mannacote’s turnkey advantages may outweigh its premium cost.
Future Trends, Adoption & Outlook
Looking forward, Mannacote’s trajectory depends on several factors:
1. R&D & Material Innovation
Continued improvement in nano-materials, smart polymers, catalyst systems, and self-healing mechanisms will be core to Mannacote staying competitive.
2. Certification & Standards
Obtaining industry approvals (e.g. for food contact, medical surfaces, marine standards) will broaden adoption.
3. Market Penetration & Awareness
More case studies, pilot projects, and success stories can convince conservative industries to adopt it.
4. Cost Reduction & Scale
Mass production, supply chain optimization, and better raw materials will help bring costs down.
5. Hybrid / Multi-domain Use
As agriculture, food science, and coatings converge (e.g. protective + nutrient delivery), Mannacote may see more crossover applications.
6. Regulatory & Environmental Pressures
As stricter environmental regulations push away high-VOC solutions, coatings like Mannacote may have an advantage if they can deliver performance with eco compliance.
In summary, Mannacote is positioned to ride the wave of smart, sustainable materials. Whether it becomes a mainstream standard or remain a niche premium solution depends on execution, certification, and real-world demonstrations.
Conclusion
Mannacote is a promising and multi-faceted concept that spans industrial coatings, sustainable agriculture, and functional coatings. In its industrial form, it delivers strong protection, durability, and (in advanced variants) smart responses to stress. In agricultural / bio contexts, it offers controlled release, edible or biodegradable coatings, and enhanced protection for seeds or produce.
But because “Mannacote” is applied in multiple fields, clarity about the variant is essential. The real test will be in long-term, real-world deployment, cost efficiency, certification, and consistent performance.